AET (ATC 16) 论文阅读
Kinetic Modeling of Data Eviction in Cache
Abstract
- In this paper, we present a kinetic model of LRU cache memory, based on the average eviction time (AET) of the cached data.
- The AET model enables fast measurement and low-cost sampling.
- It can produce the miss ratio curve (MRC) in linear time with extremely low space costs.
- Furthermore, AET is a composable model that can characterize shared cache behavior through modeling individual programs.
Introduction
AET Model
LRU Stack and Eviction Time
定义:
- arrival time Tm = the time it takes for a block to reach stack position m (from its last access)
- natually, T0 = 0, and the eviction time is Tc (block leaves position c-1)
- “condition of movement”: at each access in the eviction process, data block either stays at its current position (命中了更前的位置) or steps down one position (miss or 命中了更后的 block)
- for a simpler test, use reuse time (x stack position): “When block z is accessed, and d is at stack position m, d moves down if and only if the (backward) reuse time of z is greater than d’s arrival time Tm.”
Average Eviction Time (AET)
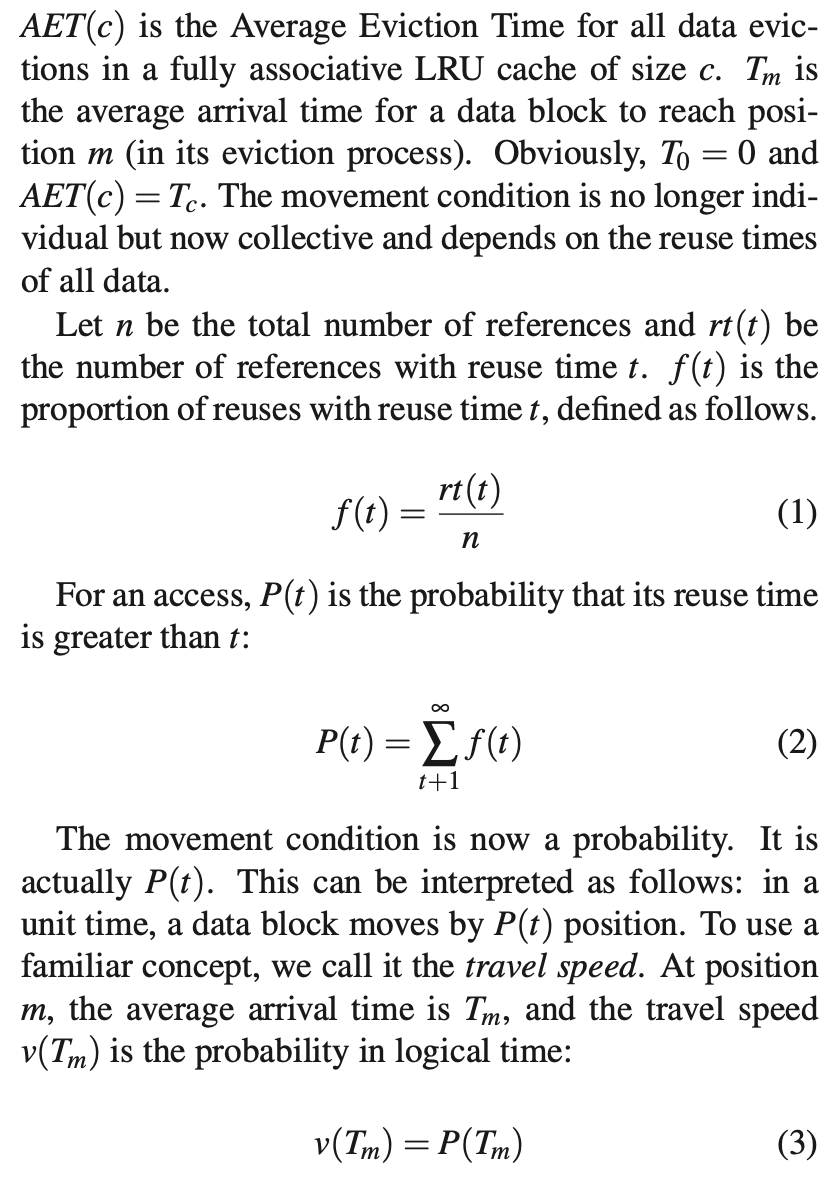
By definition, P(Tm) is monotone and non-increasing with Tm
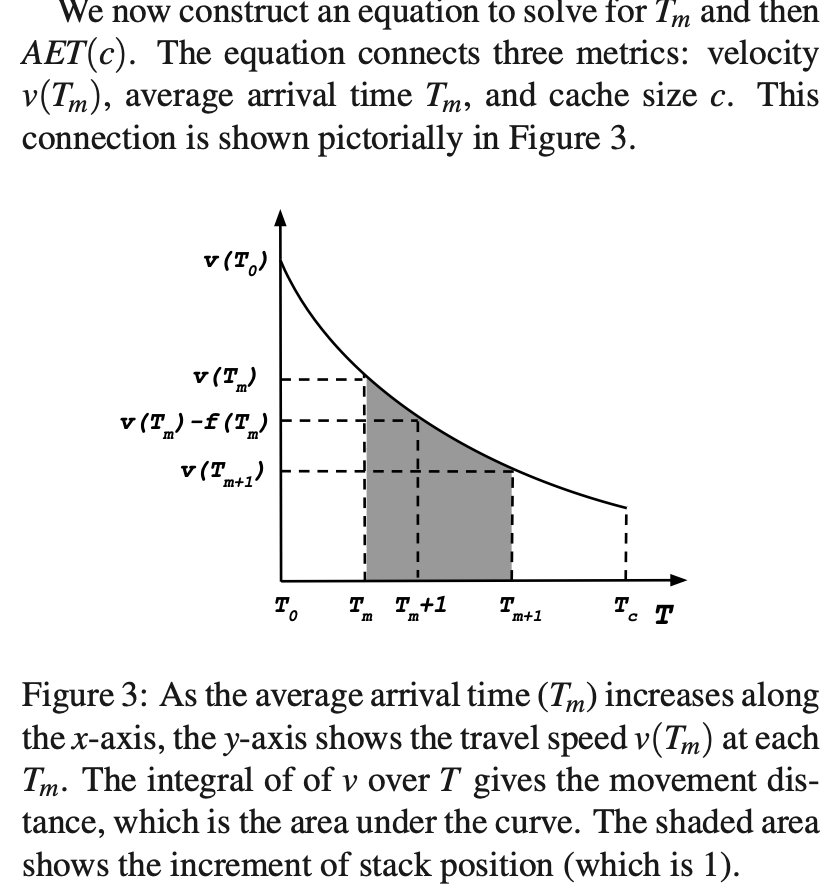
注意:最小 delta T = 1 access (temporal increment)

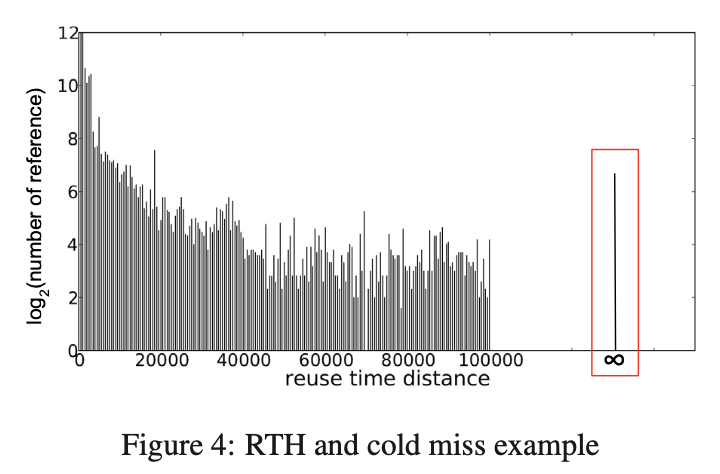
注意:cold miss 的 reuse distance 算成 ∞
Correctness
略
AET in Shared Cache
跳过
Reuse Time Histogram (RTH) Sampling
Sampling Techniques
- Address Sampling: monitor a fixed subset of the address space (某些 key 有可能有 bias)
- Fixed Interval Sampling: a subset of references (只观测一小段时间来代表整体,也有 bias)
- Random Sampling: instead of fixed sampling rate m, the distance between two adjacent monitoring points is a random value (a certain range). [StatStack]
- Reservoir Sampling: 具体怎么操作没看懂,space complexity from O(M) to O(1)
Phase Sampling
“For programs that have an unstable reference pattern, we evenly divide its execution into phases. For each phase, we use random sampling to construct the RTH and MRC for this phase. Then we construct the MRC of the entire program. The miss ratio at any cache size is average miss ratio of all MRCs at this size. We call this technique phase sampling.”
注意:上一个 phase 最后一次 reuse 记录得留到下一次 reuse
Cold Miss Handling
其实 # of cold miss 就是 # of unique keys,所以在 sampled set 也近似成这样做。
Evaluation
To save memory and make a fair comparison, we record the reuse time histogram (AET, StatStack, ABF sampling) and reuse distance histogram (Counter Stacks, SHARDS) using the compressed representation by Xiang et al. [19]. Each histogram is an array which is binned in logarithmic ranges. Each (large enough) power-of-two range is divided into (up to) 256 equal-size increments. This representation requires less than 100KB for all our workloads.
AET vs Counter Stacks

AET vs SHARDS
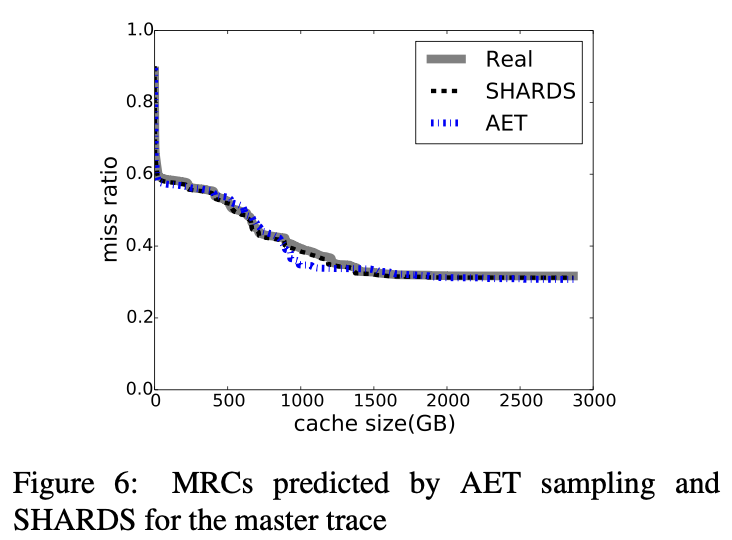
略
Related Work
评论
前半部分用 reuse time 而不是 reuse distance 的证明很漂亮