OSCA (ATC20) 论文阅读
OSCA: An Online-Model Based Cache Allocation Scheme in Cloud Block Storage Systems
Abstract
略
Introduction
cloud block storage (CBS)
- Cloud infrastructures typically employ cache servers, consisting of multiple cache instances competing for the same pool of resources.
- The currently used even-allocation policy called EAP or equal cache partitioning determines the cache requirements in advance according to the respective subscribed SLOs and then provisions cache resources for each cache instance. However, this static configuration method is often suboptimal for the cloud environment and induces resource wastage, because the cloud I/O workloads are commonly highly-skewed.
Contributions:
- online cache model based on re-access ratio (not collect+process date, but trace unique data blocks)
- total hit traffic as metric to gauge cache efficency
- search optimal configuration using dynamic programming
Background and Motivation
Cloud Block Storage
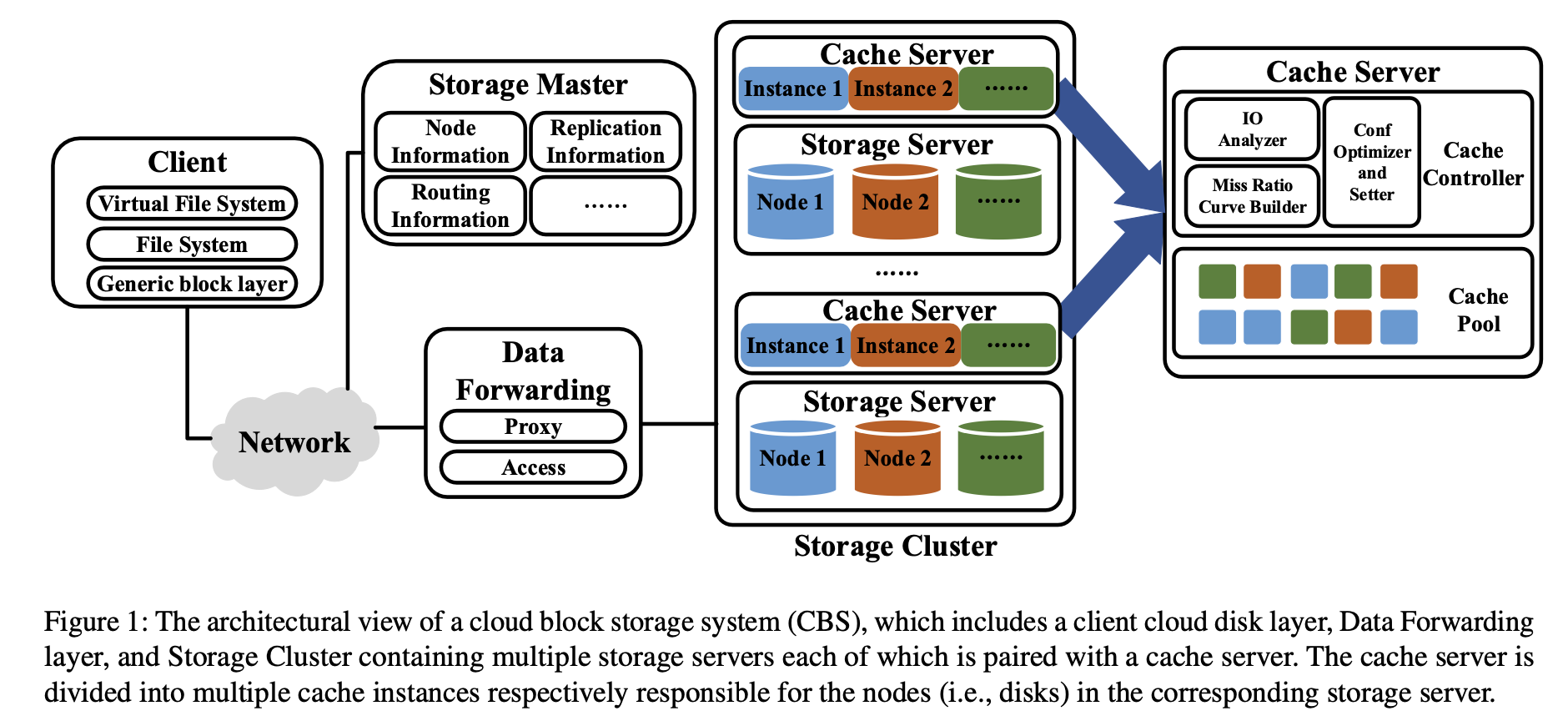
暂略
Cache Allocation Scheme
- qualitative methods (TCM, REF)
- quantitative methods, using Miss Ratio Curve (MRC) (SHARDS)
Existing Cache Modeling Methods
- Locality quantization method
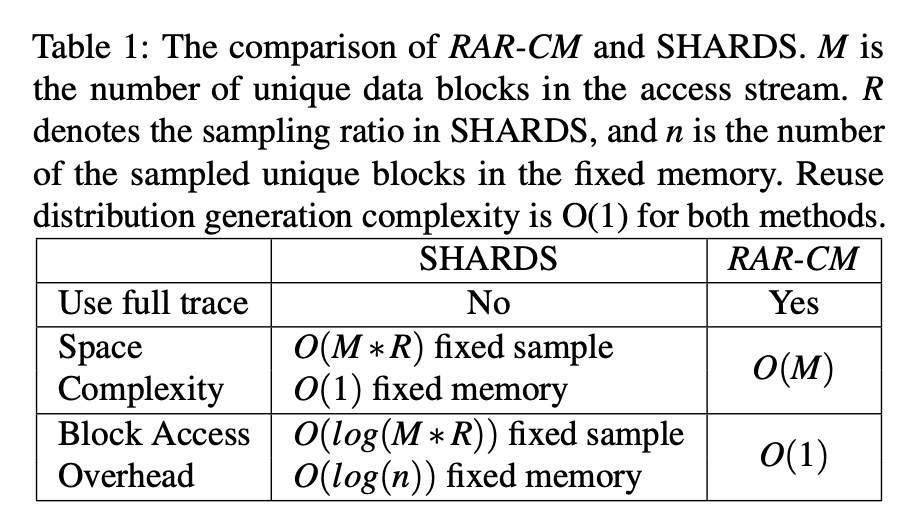
RAR-CM 相比 SHARDS 的好处是用更多的空间换时间,注意,两者都可以 online。
- Simulation-based cache modeling: concurrently run multiple simulation instances to determine the cache hit ratio in different cache sizes
Design and Implementation
Design Overview
略
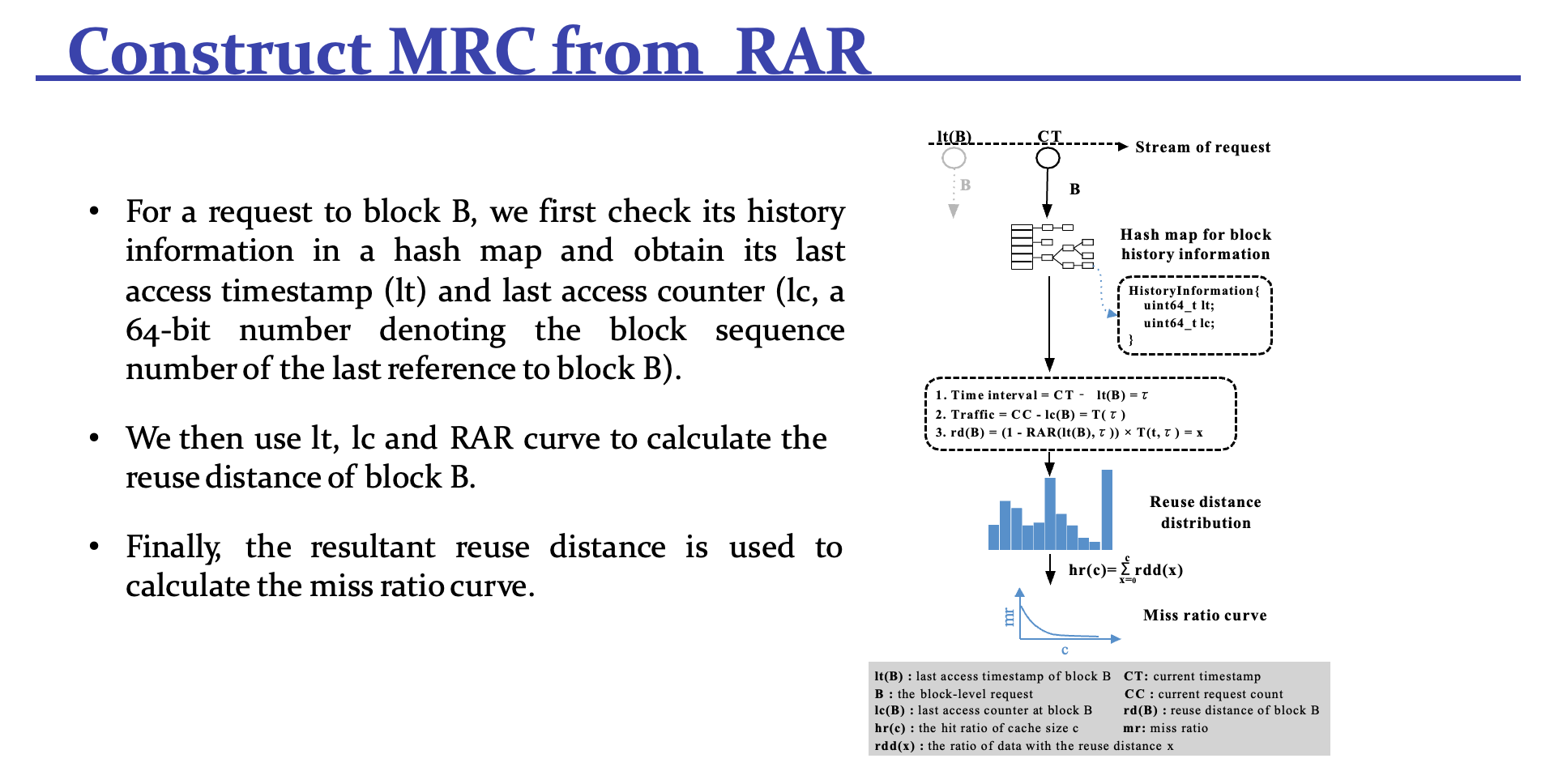
Re-access Ratio Based Cache Model
这块是重点,论文说实话看得我有点乱,引用 slides 里面的例子:
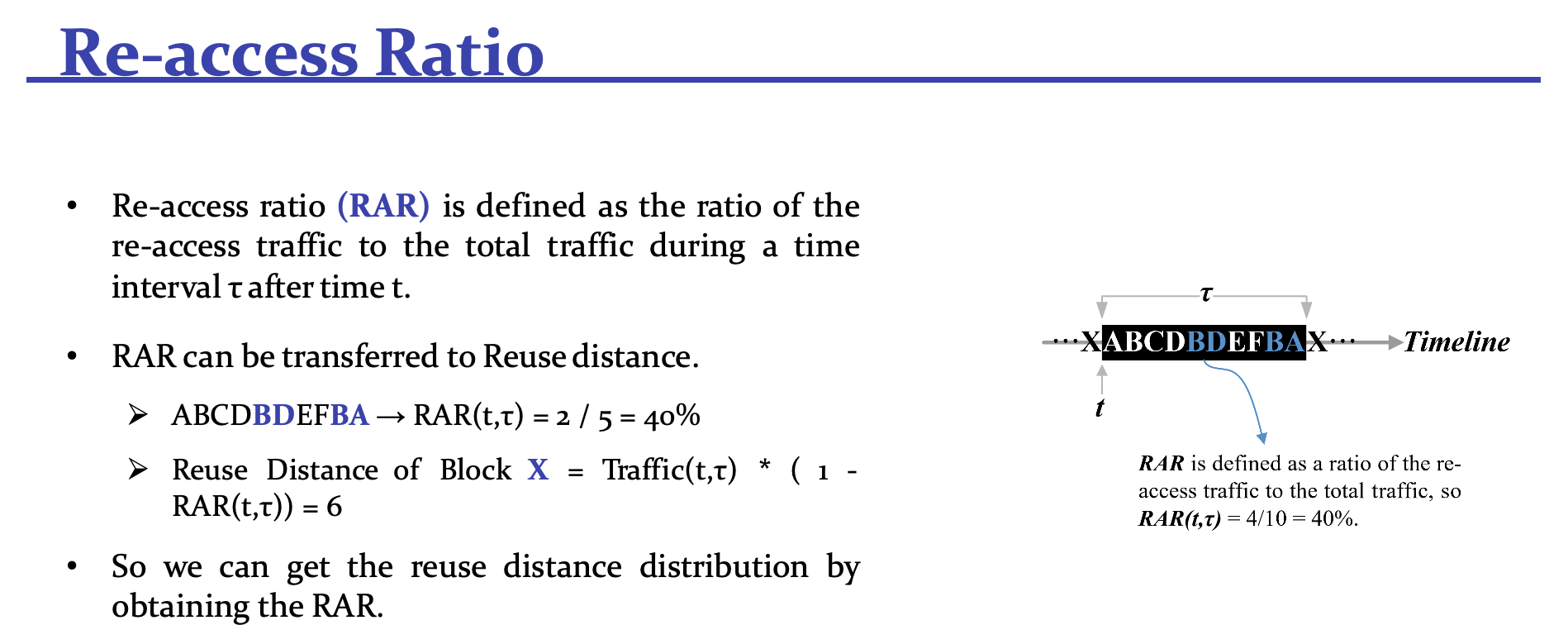
reuse distance 是一个块从上一次被挪到队头,往后移动的实际距离
那么具体如何设计实现呢?
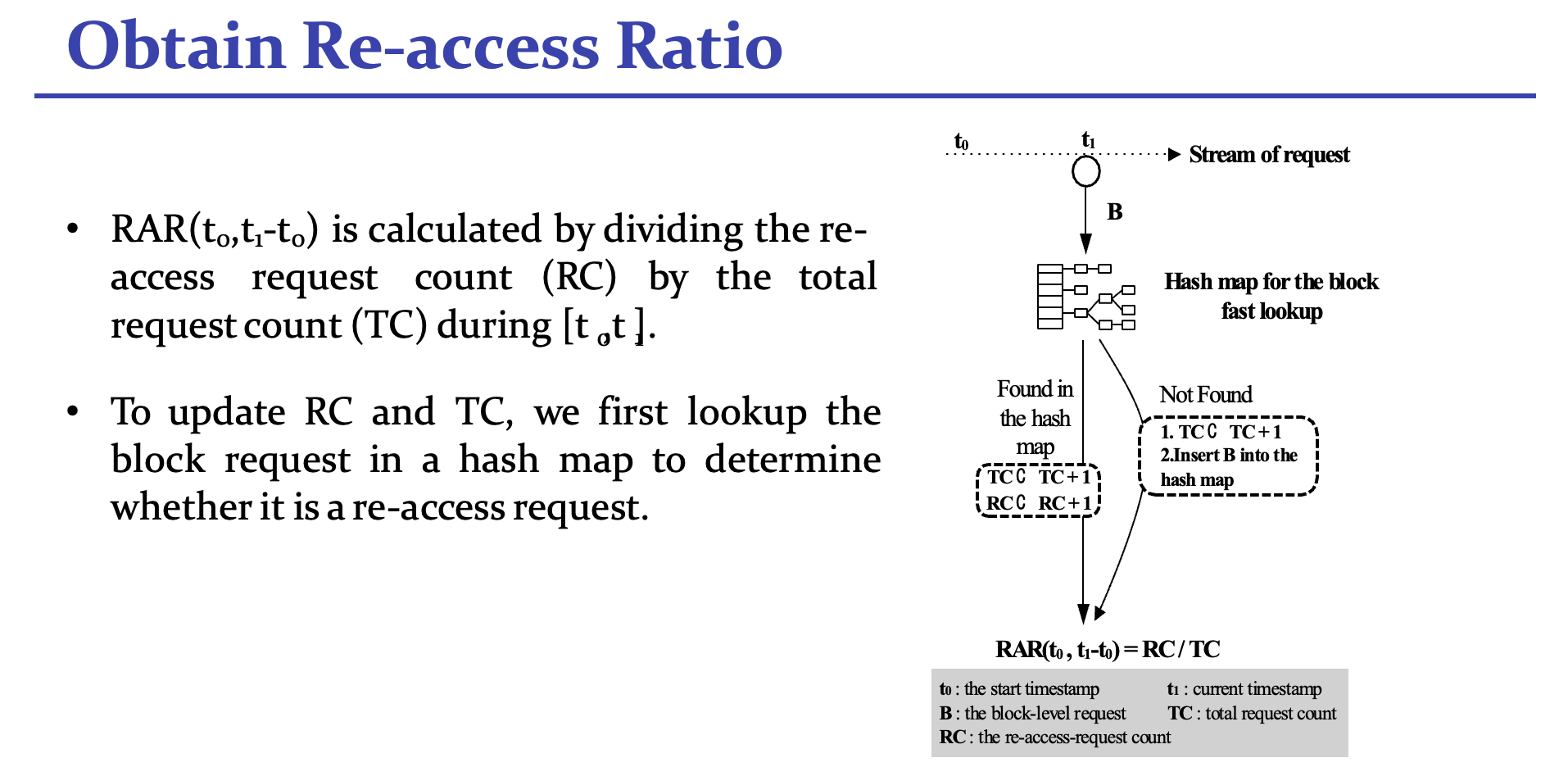
Goal: Overall hit traffic
Evaluation
略
评论
首先是几个问题:
- How to manage reuse records (hash map)?
- How to refresh start timestamp? How to do aging? (In this paper, once per day refresh or even not)
- When lots of items being evicted, how long should such records in hash map be kept? How to efficiently/sufficiently clean them?
- How fast is MRC construct? (In this paper, sequential construction)
- Maybe coarse-grained bucket is enough
本文还缺省了很多 sensitivity analysis,比如:
- DP 的速度
- MRC construction 如何 catch up dynamic workload 的?
- 等等