RLR (HPCA 21) 论文阅读
Designing a Cost-Effective Cache Replacement Policy using Machine Learning
Abstract
In this work, we use Reinforcement Learning (RL) to learn a cache replacement policy. After analyzing the learned model, we are able to focus on a few critical features that might impact system performance. Using the insights provided by RL, we successfully derive a new cache replacement policy – Reinforcement Learned Replacement (RLR). Compared to the state-of-the-art policies, RLR has low hardware overhead, and it can be implemented without needing to modify the processor’s control and data path to propagate information such as program counter.
Introduction
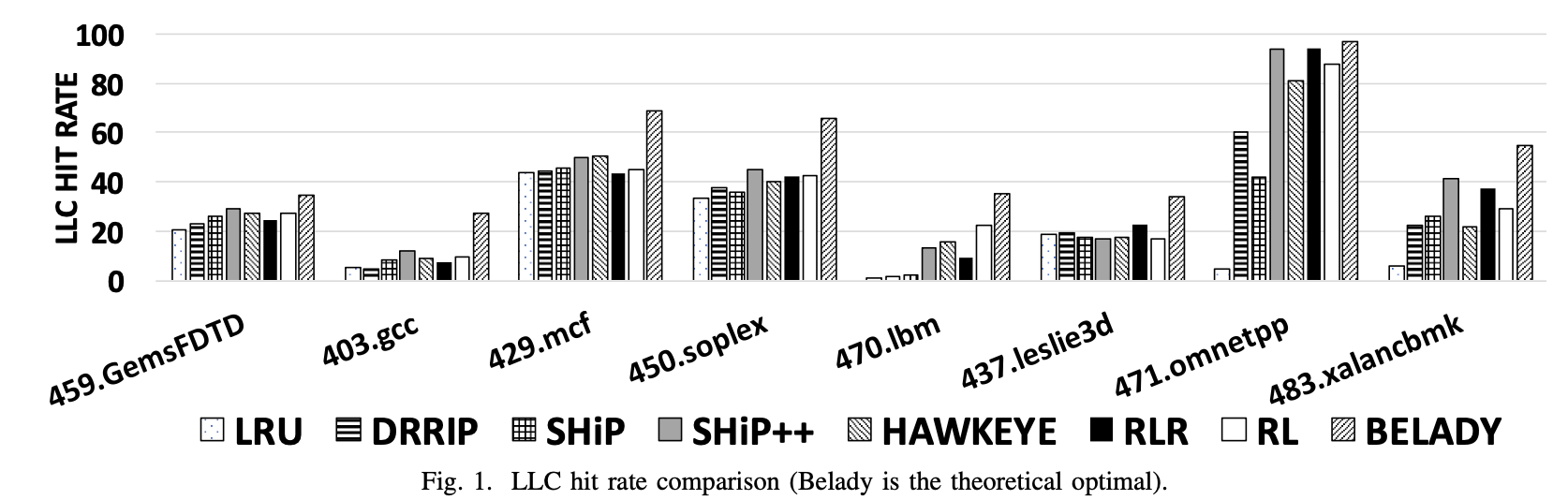
Unsurprisingly, the PC-based policies (SHiP, SHiP++, and Hawkeye) outperform non-PC-based policies (LRU and DRRIP) in almost all benchmarks.
Unfortunately, incorporating PC into the replacement policy not only requires additional storage overhead but also involves significant modifications to the processor’s control and data path. Accessing PC at the LLC requires propagating PC through all levels of the cache hierarchy, including widening the data path, modifying cache architecture to store PC, adding extra storage for PC in the Issue Queue, Reorder Buffer (ROB) and Load/Store Queue (LSQ), and more. More costly than the overhead of implementing PC- based policies is the fact that these changes require an overhaul of the entire processor pipeline, which would require significant design and verification overheads.
How can we improve the cache replacement policy without using PC?
Guided by ML, we frame a cost-effective cache replacement policy – Reinforcement Learned Replacement (RLR). Overall, RLR does not require heavy modification to the CPU microarchitecture and out- performs LRU and DRRIP for most evaluated benchmarks.
看到这,本文应该只想 outperform “cost-efficent” 这条赛道的算法。
Related Work
略,不重要
MACHINE LEARNING-AIDED ARCHITECTURE EXPLORATION
评论
先不看了,之后再说