Skyplane (NSDI 23) 论文阅读 - save egress-cost and maximize transfer speed
Skyplane: Optimizing Transfer Cost and Throughput Using Cloud-Aware Overlays
想读的原因基本在 abstract 里了:multi-cloud、egress cost、user-provided constraint。
Abstract
关注 wide-area bulk data transder 的吞吐(性能)especially inter-region
解决方法:
- adapt network overlays (routing data through indirect paths at the application layer)
- consider trade-off between price (i.e. egress cost,传数据出云的花费) and performance
- use mixed-integer linear programming (for optimal overlay path and resource allocation)
- consider user-provided constraints on price or performance
Introduction
“Increasingly, cloud applications transfer data across datacenter boundaries, both across multiple regions within a cloud provider (multi-region) and across multiple cloud providers (multi-cloud). This is in part due to privacy regulations, the availability of specialized hardware, and the desire to prevent vendor lock-in. In a recent survey [26], more than 86% of 727 respondents had adopted a multi-cloud strategy across diverse workloads.”
本文同时关注 multi-region 和 multi-cloud,并且给出了几类 motivation 来源。至于那个 survey [26],我持保留意见,据我所知,multi-cloud 仍然 too far to be used。
“How can we optimize network cost and throughput for cloud bulk transfer?”
为什么不能优化在 routing protocols in internal networks of cloud providers?
- 为 high throughput 优化的协议可能损害 low latency
- 云服务商之间并没有兴趣做自己的数据“传出”的优化 “cloud providers lack a strong incentive to optimize dara transfer to other clouds”
[定义] Overlay paths: paths that send data via intermediate regions
Overlay path 有可能更快,因为这跟每两点之间的 bandwidth 支持有关。
本文超越 overlay 这个老概念的地方在于 price 和 elasticity
- 引入价格之后,bandwidth 不再是唯一的指标(richer problem space),如图:
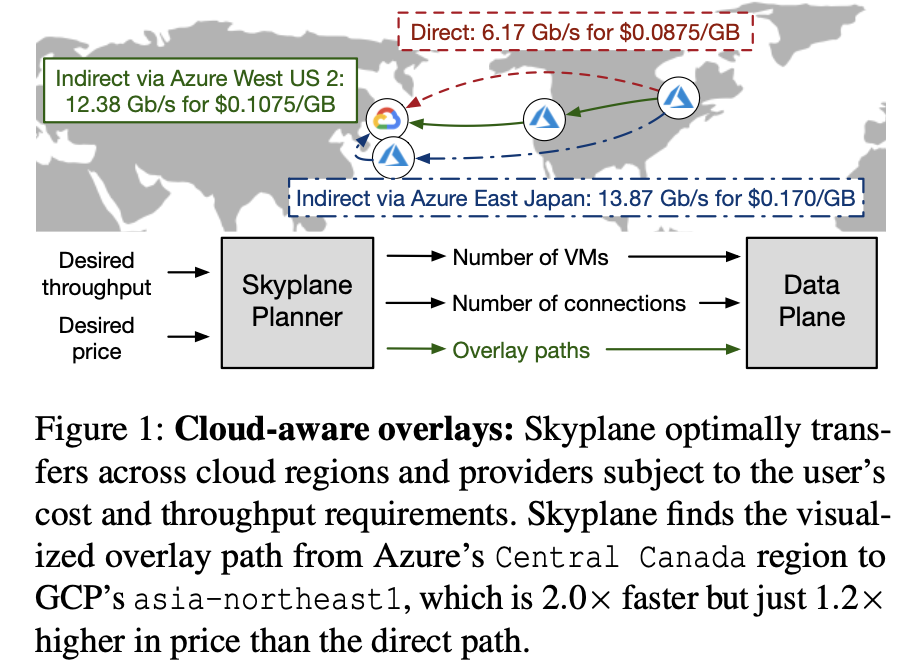
- 点与点之间的 bandwidth 不是固定的,比如增加该 region 的 VM 数量就可以提升传输的能力(richer solution space)
虽然有了更复杂的 problem/solution space,本质上还是解出 data transfer path & amount of cloud resources to allocate along that path。
Question:
-
不明白怎么做到比原生支持的传输要快 X 倍。难道是因为可以通过 overlay 增加 bandwidth?是的,比如多开 VM 用来传输
Background
- Network overlays: 这个概念专指 application 层面的 routing,此前与此相关的工作也各有各的优化目标。
- 云服务商会有 service limits。每种 instance type 会有对应的 bandwidth 约束,egress bandwidth 有可能也有一个比例上限。
- egress cost 只跟量有关,跟速率无关。
- multi-region 的 intra-cloud transfers 价格越远越高,但 multi-cloud 的 inter-cloud transfers 与地理远近无关。
- Egress prices dominate the cost of a bulk transfers. 比如,比较的是租一个 VM 和传大量数据的 egress cost。
我感觉以上的现状都会影响 pricing model 具体如何设计。
- Cloud object storage 也有自己的特点,例如:data stored immutably,consistency model各大云服务商都不同,读速率也有可能被约束
Overview of Skyplane
优化只支持两种选择:
- bandwidth subject to a price ceiling
- price subject to a bandwidth floor
Overlay formulation in Skyplane’s planner
这里引入了一个假设 high statistical multiplexing: Single user’s bandwidth usage is negligible, thus Skyplane can compute a data transfer plan without regard to other users’ bulk transfer.
Profiling cloud networks
两张图信息量足够:
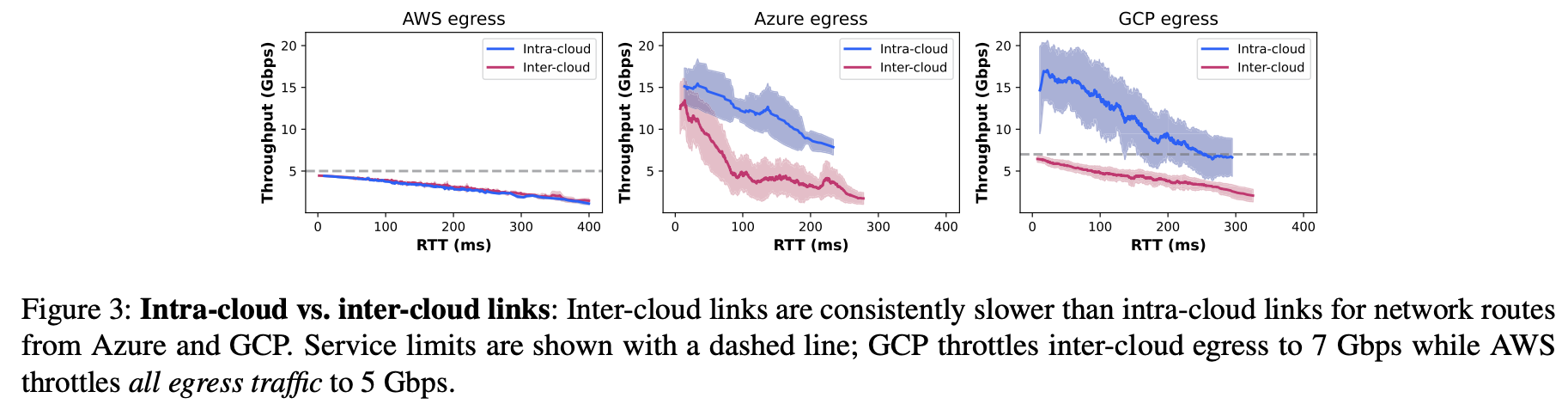
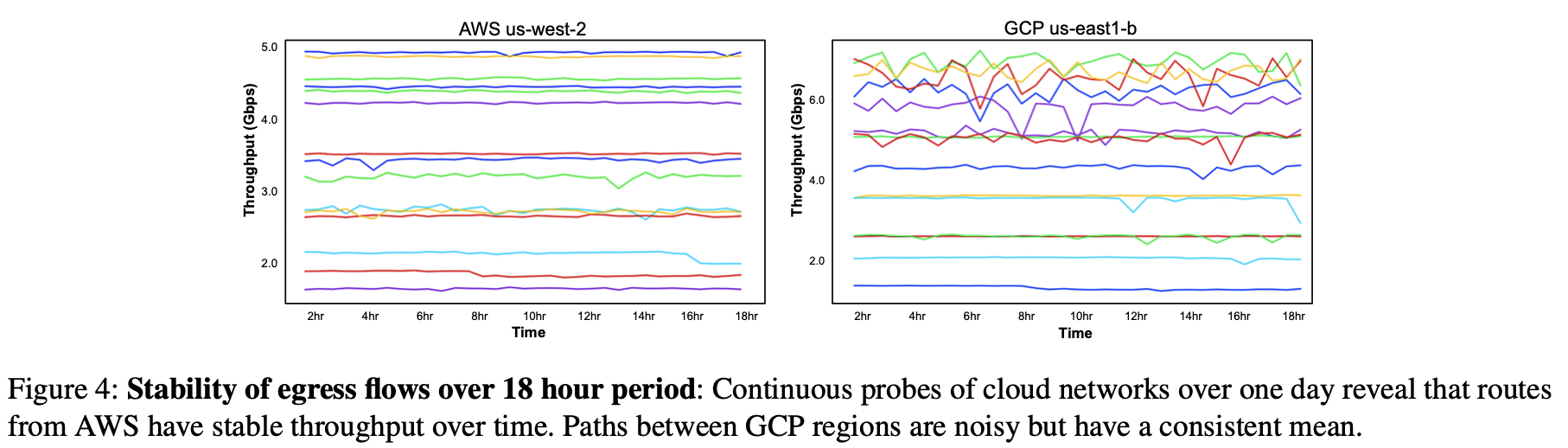
“it should be sufficient to profile networks relatively infrequently (i.e. every few days). In practice, this information could be collected by third-party service, or measured via active probing along live transfers.”
Skyplane’s data plane
不明白这段用意是啥
Principles of Skyplane’s planner
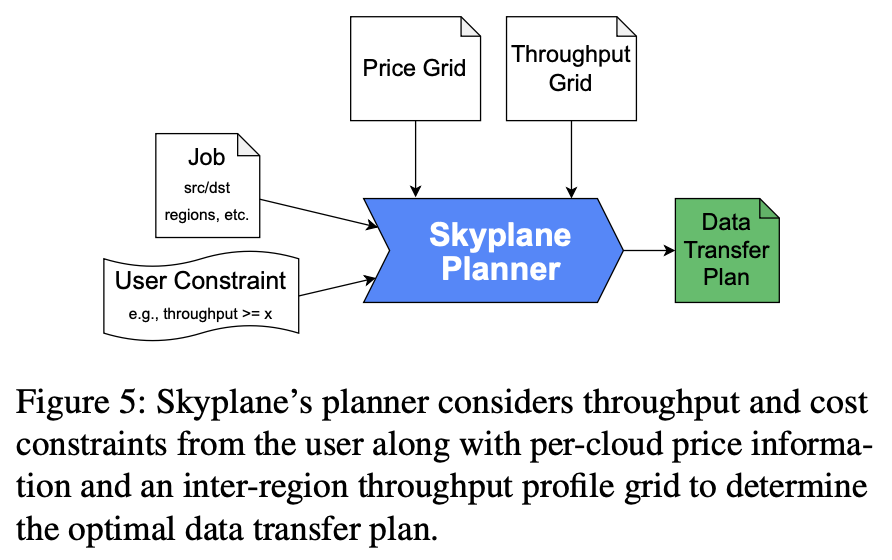
Question:
- “Note that the planner is not directly programmed to use these techniques; they are merely patterns that it discovers in the course of finding the optimal MILP solution.” ?
Achieving low instance and egress costs
Choosing the relay region
Combining multiple paths
Parallel TCP for high bandwidth
经验上放 up to 64 TCP connections
本文有一个关于 “fair share” 的讨论。
Multiple VMs for high bandwidth
Skyplane’s planner takes into account a limit on the number of instances that a user can allocate per region.
Finding optimal transfer plans
Question:
-
如果目标是 minimize cost,有什么情况会比直接点到点传输的 egress cost 要便宜?compression or 每个 provider 的不同结点也可能不一样
Objective(这段分析很有意思):
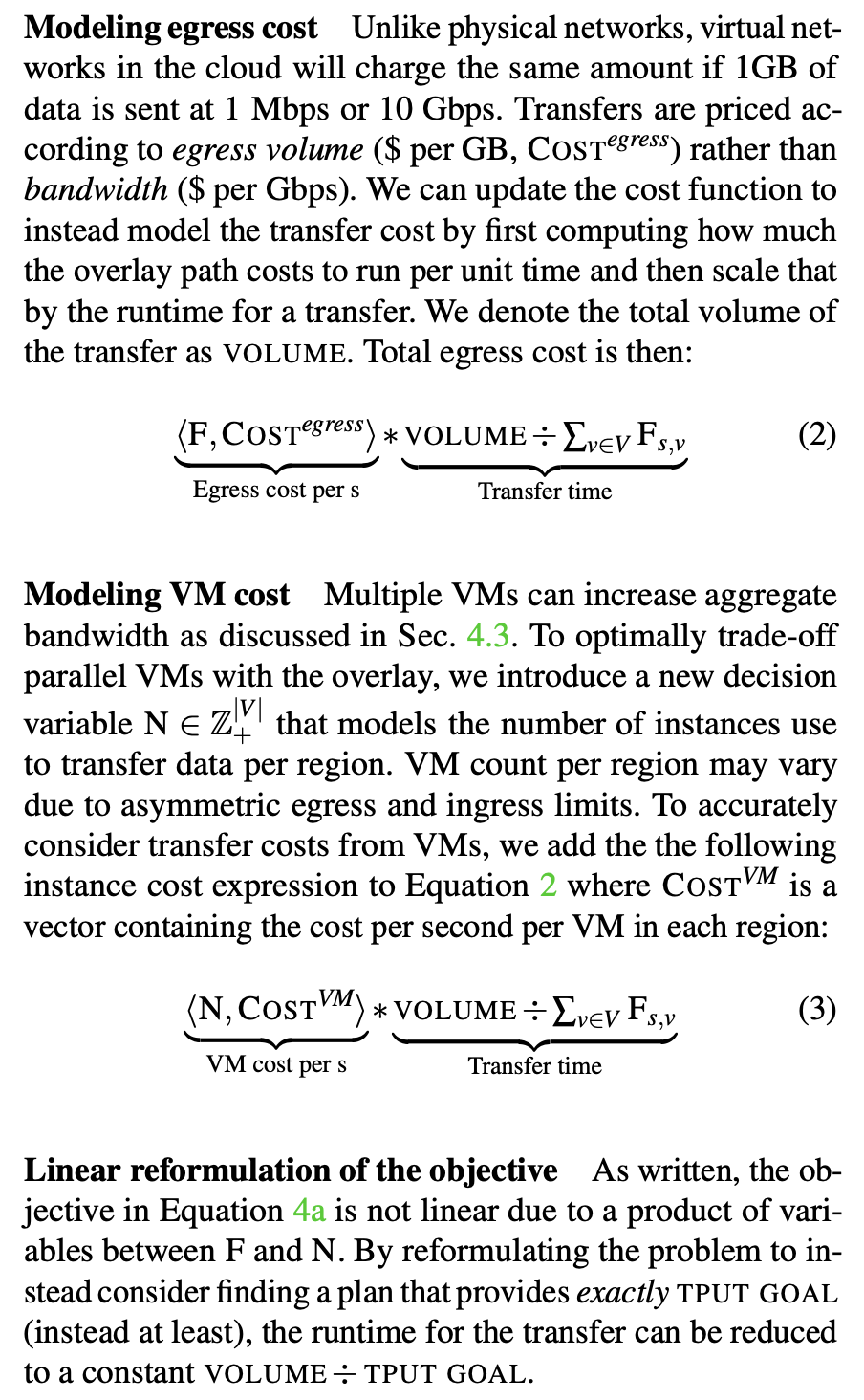
不对称性:”We can approximate a solution by solving for the minimum cost transfer plan at a range of many throughput goals. The result of this procedure is a Pareto frontier curve (as shown in Fig. 9c). A throughput maximizing solution can be extracted from this curve. The quality of approximate solution will depend on how many samples are used.”
Implementation of Skyplane
考虑了很多细节:
- 使用 Gurobi library solver,但 Coin-OR library 也能用;
- AWS 选用 m5.8xlarge instances 而非更小的 VM 是因为更小的 VM 往往有 burstable networking performance;其他(Microsoft Azure, Google Cloud)为了一致性选用了差不多大的;
- To minimize unnecessary bloat in VM images, we use compact OSes such as Bottlerocket [3] and package dependencies via Docker(没太懂);
- 假设可以分成差不多大的小块;
- 为了避免 straggler 效应,不使用现有的 round-robin 工具(GridFTP),而是看情况动态分发数据到各 TCP connections(我的理解是 Round-Robin 是 static 策略,有可能和预测不符的时候并不能自调整);
- 还要注意避免 overflow buffers at relay regions:use hop-by-hop flow control to stop reading data。这里提到了 bufferbloat problems(可能导致延迟很大)并没有被太考虑,因为 Skyplane 在意吞吐。
Evaluation
Question:
- “In certain cases, Azure AzCopy performs about as well as Skyplane. We chose the koreacentral region because we expected the greatest improvements from the overlay in that region; however, storage overheads (the “thatched” regions of the bars), not networking overheads, dominated the runtime. It is possible that AzCopy avoids the Azure Blob Storage I/O overhead that dominates Skyplane’s transfer time by leveraging Azure’s Copy Blob From URL API call to download data directly into the servers running Azure Blob Storage [11].” 好像是说内部已经有优化做的比较好了
- Figure7 的 egress limit 是怎么设置的?为什么 limit 是一个 bandwidth?
- Skyplane w/o overlay 比 baseline 多了些什么来着?price model?
这里定义了一个 transfer bottleneck (utilization is over 99%),在整个链路上可以不止一处满足 bottleneck 定义。Skyplane 看到 source link bottlenecks 减少,另一边 source VM & overlay link 上升。
没看懂这几个 baseline 的情况
评论
本文整体有倾向是多花一点钱,能提升极大的 bandwidth,其实并不能怎么关注省钱。