JEDI (IMC 22) 论文阅读
JEDI: Model-driven Trace Generation for Cache Simulations
What you should know
视角是:为想要开源 trace 又害怕泄露 PII (personal identifiable information) 的“公司”视角做 trace (re-)generation。
model 叫 Popularity-Size Footprint Descriptor (pFD),同时做到 request hit ratio (RHR) & byte hit ratio (BHR) 准确,需要 LRU 算法,但是 eval 里面看到 non-LRU 也还不错。
有趣的是,本文 claim 需要用绝对数值的 Popularity 数字而非 normalized 之后的某个百分比来产生 synthetic trace,因为
Popularity distribution (POP) We define popularity of an object as the number of requests made for it in a given trace. Specifically, the popularity distribution POP(p) gives us the probability that an object is requested p times in the duration of the trace. Observe that popularity of an object depends on the length of the trace that is collected. If the length is doubled, the popularity of some objects in the trace could increase. However, we chose not to normalize the popularity by the trace length for the following reason. For sufficiently large traces, we find that there exist very few objects that are requested through the span of the trace. Most objects have a short lifespan i.e., the first and last request for an object are not far apart. Thus, if the trace is sufficiently large, POP remains unchanged as its length is increased.
结合本文的 goal 是重新生成一个接近的 synthetic trace,所以目前的版本不支持生成更长的 trace。
算法如下 Synthetic trace generator:

// 其实还有一部分是如何 mix traces 如果不止一个,这个我暂时用不上就忽略了。
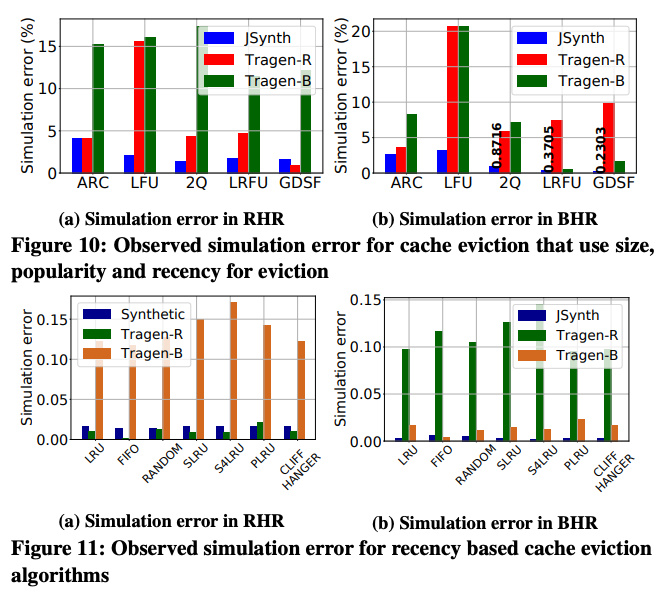
一些 eval,比如 Figure 10 & 11 展示了各种算法效果都还不错(注意:JSynth 是本文的结果,其他是 baseline)