LAMA (ATC 15) 论文阅读
LAMA: Optimized Locality-aware Memory Allocation for Key-value Cache
Abstract
以前有 slab calcification 问题。
This paper introduces locality-aware memory allocation (LAMA), which solves the problem by first analyzing the locality of the Memcached requests and then repartitioning the memory to minimize the miss ratio and the average response time.
Introduction
slab allocation 背景知识:
Memcached splits the memory cache space into different classes to store variable-sized objects as items. Initially, each class obtains its own memory space by requesting free slabs, 1MB each, from the allocator. Each allocated slab is divided into slots of equal size. According to the slot size, the slabs are categorized into different classes, from Class 1 to Class n, where the slot size increases exponentially.
目前的问题是 slab calcification 未能得到很好的解决:In the presence of workload changing, default Memcached server may suffer from a problem called slab calcification, in which the allocation cannot be adjusted to fit the change of access pattern as the old slab allocation may not work well for the new workload.
解决方法是为每个 class 产生 MRC,之后平衡 space allocation:
This study provides a low-overhead yet accurate method to model data locality and generate miss ratio curves (MRCs). With MRCs for all classes, the overall Memcached performance can be modelled in terms of different class space allocations, and it can be optimized by adjusting individual classes’ allocation.
Background
Memory Allocation in Memcached
五个现有的算法都有点差的惊人:
- Memcached Default Design: based on the number of items arriving in different classes during the cold start period
- 不能对抗任何 workload 变化
- Automove: In every 10 seconds window, if a class takes the highest number of evictions in three consecutive monitoring windows, a new slab is reassigned to it; the new slab is taken from the class that has no evictions in the last three monitoring stages.
- 需要 30 秒连续没有访问的 class 存在才能做 eviction
- Twitter Policy: random eviction, aggressive
- Periodic Slab Allocation (PSA): the number of requests of Class i is denoted as Ri and the number of slabs allocated to it is denoted as Si. The risk of moving one slab away from Class i is denoted as Ri/Si. Every M misses, PSA moves one slab from the class with the lowest risk to the class with the largest number of misses.
- 问题是这两个 metrics 不一致,low risk(访问数的平均数)和 high miss(不命中的总数)可能是同一些 classes
- Facebook Policy [age balancing]: if a class is currently evicting items, and the next item to be evicted was used at least 20% more recently than the average least recently used item of all other classes, this class is identified as needing more memory (其实是 approximate LRU)
The Footprint Theory
略
Locality-aware Memory Allocation
Goal 是 miss ratio (MR) 或者 average request time (ART)
用 dynamic programming 解 “The time complexity of the optimization is O(n * MAX2), where n is the number of size classes and MAX is the total number of slabs.”
这里有嵌套另一篇文章的 MRC 公式,我得补一下原论文。
Evaluation
这部分很有意思:”The MRC analysis is performed by a separate thread. Each analysis samples recent 20 million requests which are stored using a circular buffer. The buffer is shared by all Memcached threads and protected by a mutex lock for atomic access. During the analysis, it uses a hash table to record the last access time. The cost depends on the size of the items being analyzed. It is 3% - 4% of all memory depending for the workload we use.” 对于高吞吐压力的情况,这个 circular buffer 是 sequential 结构,可能带来不小的延迟/等待。
结果首先注意到 miss rate 和 response time 趋势很近,符合预期;其次 Twemcache 的 random policy 表现不佳,default 和几乎不怎么移动的 automove 表现也不佳;Facebook 的 age balancing 应该说比较间接,表现排在中间的样子;PSA 是和 LAMA 表现得最接近的 baseline,也说明 low risk 和 high miss count 作为 metrics 挺好的:
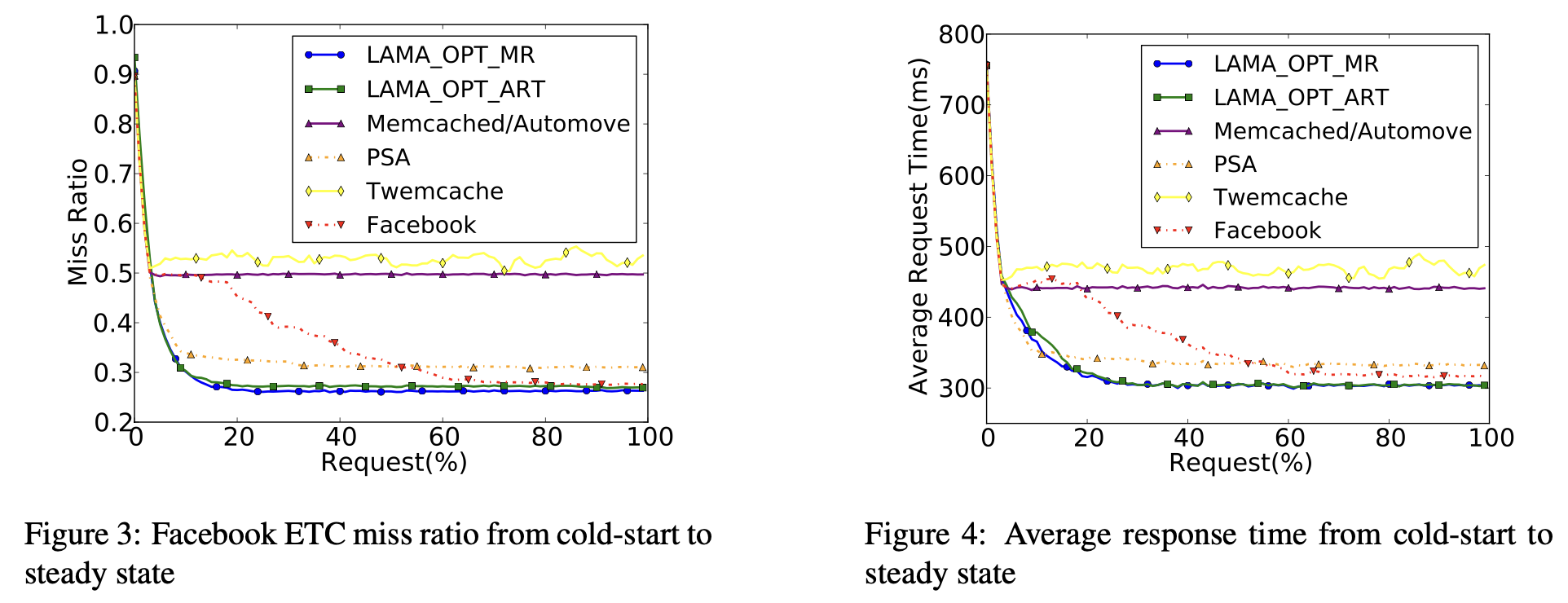
另一个值得注意的是 LAMA 有两个略显丑陋的参数,the repartitioning interval M, which is the number of items accesses before repartitioning; and the reassignment upper bound N, which is the maximal number of slabs reassigned at repartitioning。
LAMA 还声称 MRC overhead 很小,相比 reuse-distance-based MRC generation(但没说具体用了什么 RD 算法),这个算法复杂度我下一篇文章对比一下:
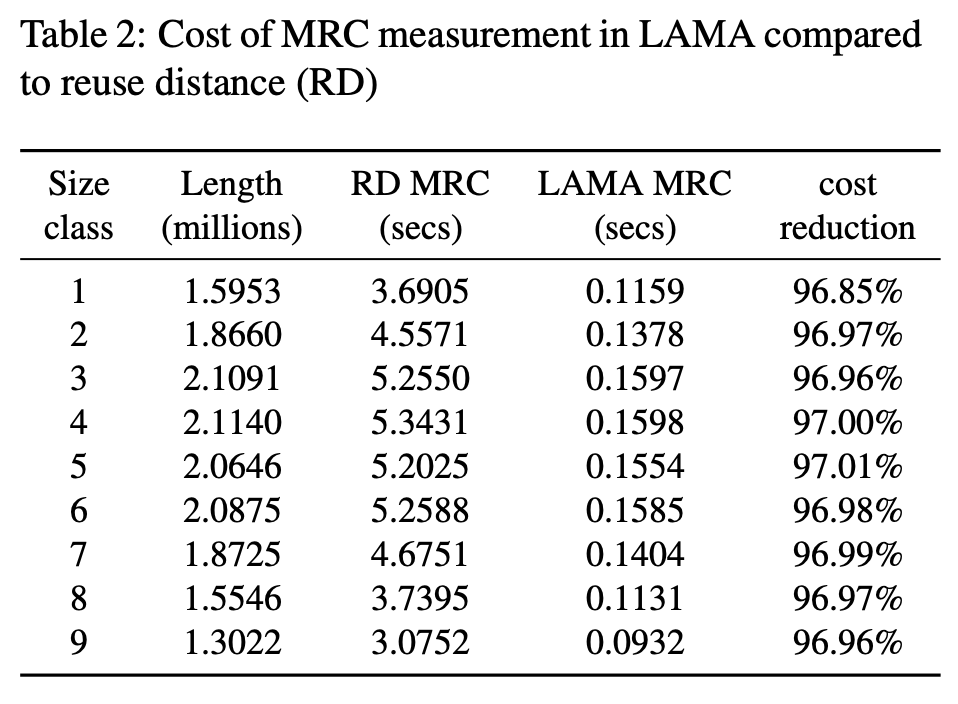
评论
我是当作一篇工程文章看的。虽然 target 在 Memcached 已经看到的很大的收益,但是如果能 claim larger impact,比如说,有没有可能 MRC + DP 可以做得更有应用场景呢?反正我如果要用 MRC + DP 解什么问题,我会考虑这篇文章的处理思路以及观察到的效果。