publications
publications by categories in reversed chronological order.
2025
-
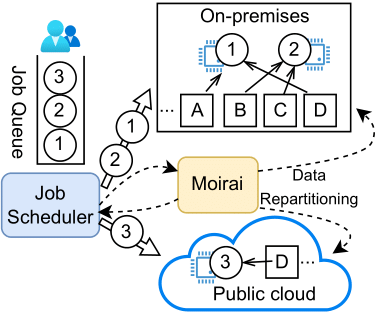 Moirai: Optimizing Placement of Data and Compute in Hybrid CloudsZiyue Qiu, Hojin Park, Jing Zhao, Yu-Kai Wang, Arnav Balyan, Gurmeet Singh, Yangjun Zhang, Suqiang (Jack) Song, Gregory R. Ganger, and George Amvrosiadis2025
Moirai: Optimizing Placement of Data and Compute in Hybrid CloudsZiyue Qiu, Hojin Park, Jing Zhao, Yu-Kai Wang, Arnav Balyan, Gurmeet Singh, Yangjun Zhang, Suqiang (Jack) Song, Gregory R. Ganger, and George Amvrosiadis2025The deployment of large-scale data analytics between on-premise and cloud sites, i.e., hybrid clouds, requires careful partitioning of both data and computation to avoid massive networking costs. We present Moirai, a cost-optimization framework that analyzes job accesses and data dependencies and optimizes the placement of both in hybrid clouds. Moirai informs the job scheduler of data location and access predictions, so it can determine where jobs should be executed to minimize data transfer costs. Our optimizer achieves scalability and cost efficiency by exploiting recurring jobs to identify data dependencies and job access characteristics and reduces the search space by excluding data not accessed recently.We validate Moirai using 4-month traces that span 66.7M queries accessing 13.3EB from Presto and Spark clusters deployed at Uber, a multi-national transportation company leveraging large-scale data analytics for its operations. Moirai reduces hybrid cloud deployment costs by over 97% relative to the state-of-the-art partitioning approach from Alibaba and other public approaches. The savings come from 95–99.5% reduction in cloud egress, up to 99% reduction in replication, and 89–98% reduction in on-premises network infrastructure requirements. We also describe concrete steps being taken towards deploying Moirai in production.
2024
-
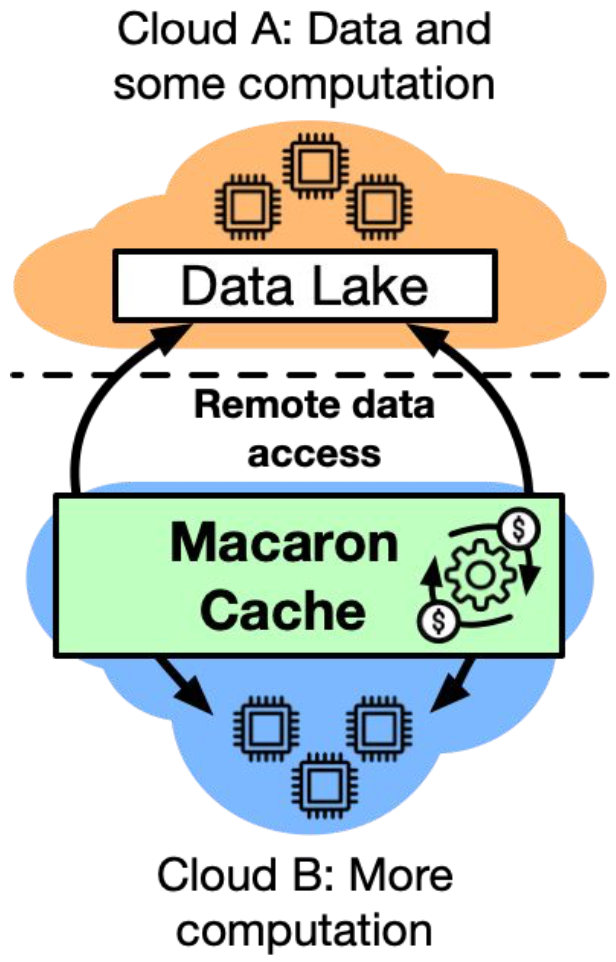 Reducing Cross-Cloud/Region Costs with the Auto-Configuring MACARON CacheHojin Park, Ziyue Qiu, Gregory R. Ganger, and George Amvrosiadis2024
Reducing Cross-Cloud/Region Costs with the Auto-Configuring MACARON CacheHojin Park, Ziyue Qiu, Gregory R. Ganger, and George Amvrosiadis2024An increasing demand for cross-cloud and cross-region data access is bringing forth challenges related to high data transfer costs and latency. In response, we introduce Macaron, an auto-configuring cache system designed to minimize cost for remote data access. A key insight behind Macaron is that cloud cache size is tied to cost, not hardware limits, shifting the way we think about cache design and eviction policies. Macaron dynamically configures cache size and utilizes a mix of cloud storage types to adapt to workload changes and reduce costs. We demonstrate that Macaron reduces cross-cloud workload costs by 65% and cross-region costs by 67%, mainly by reducing outgoing data transfer and by leveraging object storage alongside DRAM to reduce capacity cost.
- Data Caching for Enterprise-Grade Petabyte-Scale OLAPChunxu Tang, Bin Fan, Jing Zhao, Chen Liang, Yi Wang, Beinan Wang, Ziyue Qiu, Lu Qiu, Bowen Ding, Shouzhuo Sun, Saiguang Che, Jiaming Mai, Shouwei Chen, Yu Zhu, Jianjian Xie, Yutian (James) Sun, Yao Li, Yangjun Zhang, Ke Wang, and Mingmin ChenJul 2024
With the exponential growth of data and evolving use cases, petabyte-scale OLAP data platforms are increasingly adopting a model that decouples compute from storage. This shift, evident in organizations like Uber and Meta, introduces operational challenges including massive, read-heavy I/O traffic with potential throttling, as well as skewed and fragmented data access patterns. Addressing these challenges, this paper introduces the Alluxio local (edge) cache, a highly effective architectural optimization tailored for such environments. This embeddable cache, optimized for petabyte-scale data analytics, leverages local SSD resources to alleviate network I/O and API call pressures, significantly improving data transfer efficiency. Integrated with OLAP systems like Presto and storage services like HDFS, the Alluxio local cache has demonstrated its effectiveness in handling large-scale, enterprise-grade workloads over three years of deployment at Uber and Meta. We share insights and operational experiences in implementing these optimizations, providing valuable perspectives on managing modern, massive-scale OLAP workloads.
2023
-
 FrozenHot Cache: Rethinking Cache Management for Modern HardwareJul 2023
FrozenHot Cache: Rethinking Cache Management for Modern HardwareJul 2023Caching is crucial for accelerating data access, employed as a ubiquitous design in modern systems at many parts of computer systems. With increasing core count, and shrinking latency gap between cache and modern storage devices, hit-path scalability becomes increasingly critical. However, existing production in-memory caches often use list-based management with promotion on each cache hit, which requires extensive locking and poses a significant overhead for scaling beyond a few cores. Moreover, existing techniques for improving scalability either (1) only focus on the indexing structure and do not improve cache management scalability, or (2) sacrifice efficiency or miss-path scalability.Inspired by highly skewed data popularity and short-term hotspot stability in cache workloads, we propose Frozen-Hot, a generic approach to improve the scalability of list-based caches. FrozenHot partitions the cache space into two parts: a frozen cache and a dynamic cache. The frozen cache serves requests for hot objects with minimal latency by eliminating promotion and locking, while the latter leverages the existing cache design to achieve workload adaptivity. We built FrozenHot as a library that can be easily integrated into existing systems. We demonstrate its performance by enabling FrozenHot in two production systems: HHVM and RocksDB using under 100 lines of code. Evaluated using production traces from MSR and Twitter, FrozenHot improves the throughput of three baseline cache algorithms by up to 551%. Compared to stock RocksDB, FrozenHot-enhanced RocksDB shows a higher throughput on all YCSB workloads with up to 90% increase, as well as reduced tail latency.
- S3-FIFOFIFO Queues Are All You Need for Cache EvictionJuncheng Yang, Yazhuo Zhang, Ziyue Qiu, Yao Yue, and Rashmi VinayakJul 2023
As a cache eviction algorithm, FIFO has a lot of attractive properties, such as simplicity, speed, scalability, and flash-friendliness. The most prominent criticism of FIFO is its low efficiency (high miss ratio).In this work, we demonstrate a simple, scalable FIFO-based algorithm with three static queues (S3-FIFO). Evaluated on 6594 cache traces from 14 datasets, we show that S3-FIFO has lower miss ratios than state-of-the-art algorithms across traces. Moreover, S3-FIFO’s efficiency is robust — it has the lowest mean miss ratio on 10 of the 14 datasets. FIFO queues enable S3-FIFO to achieve good scalability with 6\texttimes higher throughput compared to optimized LRU at 16 threads.Our insight is that most objects in skewed workloads will only be accessed once in a short window, so it is critical to evict them early (also called quick demotion). The key of S3-FIFO is a small FIFO queue that filters out most objects from entering the main cache, which provides a guaranteed demotion speed and high demotion precision.
- QDLPFIFO Can Be Better than LRU: The Power of Lazy Promotion and Quick DemotionJuncheng Yang, Ziyue Qiu, Yazhuo Zhang, Yao Yue, and K. V. RashmiJul 2023
LRU has been the basis of cache eviction algorithms for decades, with a plethora of innovations on improving LRU’s miss ratio and throughput. While it is well-known that FIFO-based eviction algorithms provide significantly better throughput and scalability, they lag behind LRU on miss ratio, thus, cache efficiency.We performed a large-scale simulation study using 5307 block and web cache workloads collected in the past two decades. We find that contrary to what common wisdom suggests, some FIFO-based algorithms, such as FIFO-Reinsertion (or CLOCK), are, in fact, more efficient (have a lower miss ratio) than LRU. Moreover, we find that qick demotion — evicting most new objects very quickly — is critical for cache efficiency. We show that when enhanced by qick demotion, not only can state-of-the-art algorithms be more efficient, a simple FIFO-based algorithm can outperform five complex state-of-the-art in terms of miss ratio.
- Rethinking the Cloudonomics of Efficient I/O for Data-Intensive Analytics ApplicationsChunxu Tang, Yi Wang, Bin Fan, Beinan Wang, Shouwei Chen, Ziyue Qiu, Chen Liang, Jing Zhao, Yu Zhu, Mingmin Chen, and Zhongting HuJul 2023